LeetCode-1610-可见点的最大数目
题目
给你一个点数组 points 和一个表示角度的整数 angle,你的位置是 location,其中 location = [posx, posy] 且 points[i] = [xi, yi] 都表示 X-Y 平面上的整数坐标。
最开始,你面向东方进行观测。你 不能 进行移动改变位置,但可以通过 自转 调整观测角度。换句话说,posx 和 posy 不能改变。你的视野范围的角度用 angle 表示,这决定了你观测任意方向时可以多宽。设 d 为你逆时针自转旋转的度数,那么你的视野就是角度范围 [d - angle/2, d + angle/2] 所指示的那片区域。
对于每个点,如果由该点、你的位置以及从你的位置直接向东的方向形成的角度 位于你的视野中,那么你就可以看到它。
同一个坐标上可以有多个点。你所在的位置也可能存在一些点,但不管你的怎么旋转,总是可以看到这些点。同时,点不会阻碍你看到其他点。
返回你能看到的点的最大数目。
示例
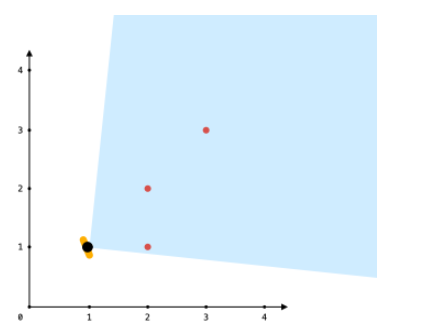
输入:points = [[2,1],[2,2],[3,3]], angle = 90, location = [1,1]
输出:3
解释:阴影区域代表你的视野。在你的视野中,所有的点都清晰可见,尽管 [2,2] 和 [3,3] 在同一条直线上,你仍然可以看到 [3,3] 。
输入:points = [[2,1],[2,2],[3,4],[1,1]], angle = 90, location = [1,1]
输出:4
解释:在你的视野中,所有的点都清晰可见,包括你所在位置的那个点。
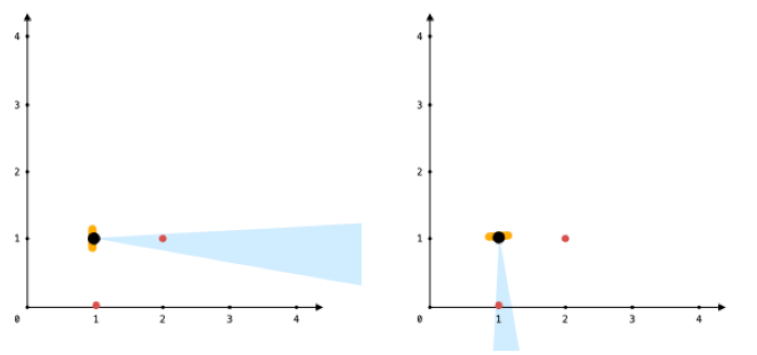
输入:points = [[1,0],[2,1]], angle = 13, location = [1,1]
输出:1
解释:如图所示,你只能看到两点之一。
解答
好难嗷
update: 2021.12.18
你的视野范围是有限的只能看到 angle 范围内的东西,给你一个位置和许多东西,你可以通过旋转来看这些东西,但是你必须站在这个位置不能移动。
将所给的点全部转换为以location为原点的坐标,这样一来就很方便可以知道可以看到的点的位置了。
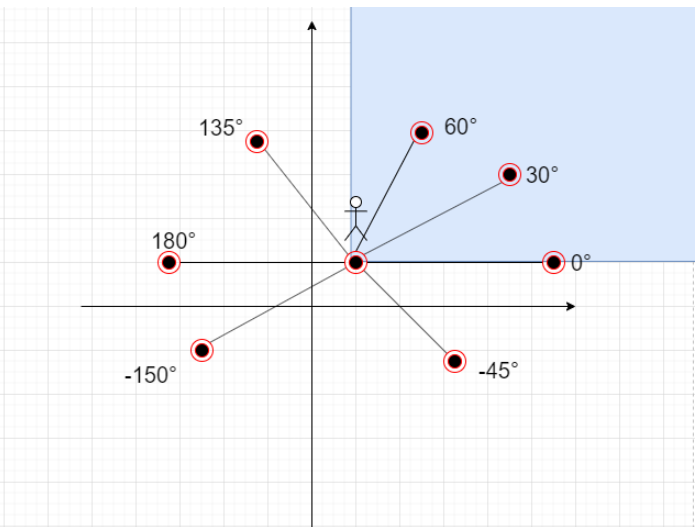
但是有一个很坑的地方就是location和 points 中的point可能会重合,所以我们要对与location重合的点进行重新判断,这些点肯定是能看到的。
剩下计算两个 points 中point的点位于location的极角,在这里又有一个很坑的地方,我们使用的方法atan2方法返回的极角范围如下
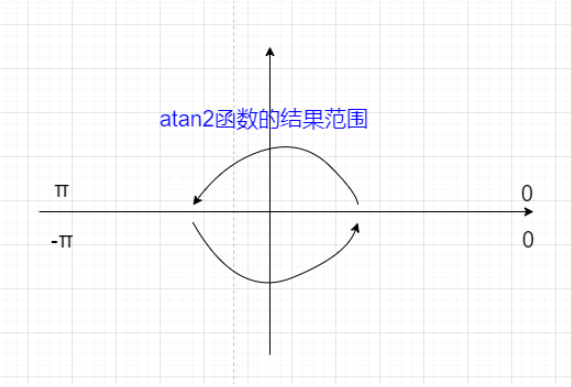
当我们旋转到超过 PI 时,就不行了。这里可以将所有的极角同时 +360°,这样可以保证极角是单调的。
最后用窗口为angle来找到最终的结果
代码
int test(vector<vector<int>> &points, int angle, vector<int> &location){
// 与 location 重合的点个数
int sameCnt = 0;
vector<double> polarDegrees;
for (auto & point : points) {
if (point[0] == location[0] && point[1] == location[1]) {
sameCnt++;
continue;
}
double degree = atan2(point[1] - location[1], point[0] - location[0]);
polarDegrees.emplace_back(degree);
}
// 将计算的极角排序
sort(polarDegrees.begin(), polarDegrees.end());
int m = polarDegrees.size();
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
polarDegrees.emplace_back(polarDegrees[i] + 2 * M_PI);
}
int maxCnt = 0;
int right = 0;
double degree = angle * M_PI / 180;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
while (right < polarDegrees.size() && polarDegrees[right] <= polarDegrees[i] + degree) {
right++;
}
maxCnt = max(maxCnt, right - i);
}
return maxCnt + sameCnt;
}